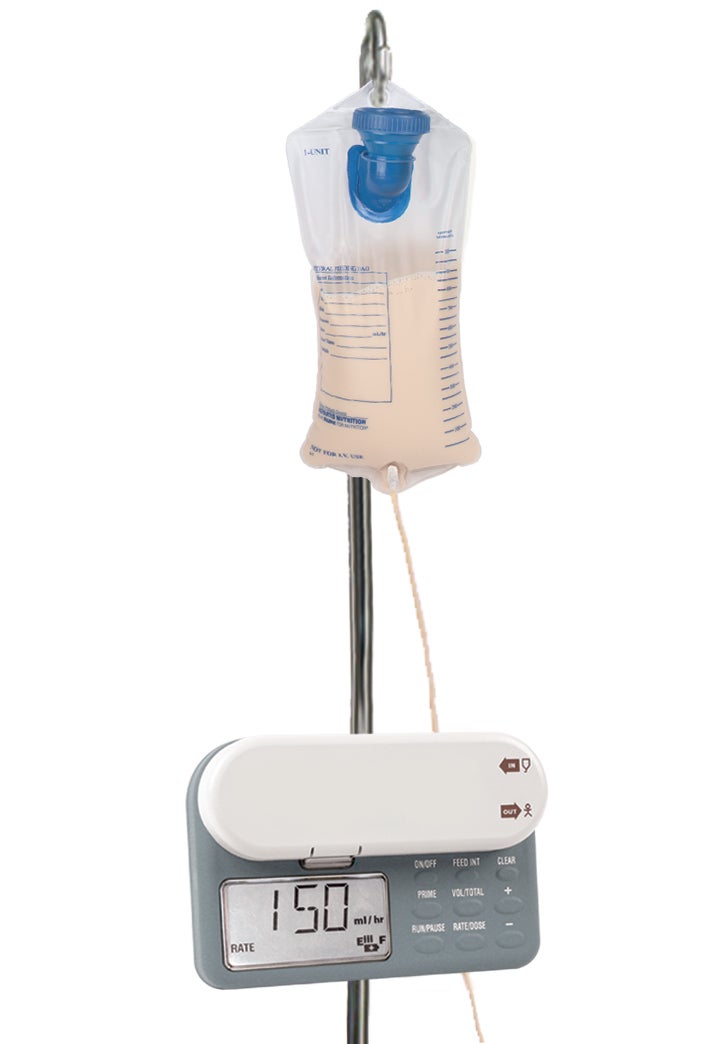
A feeding pump is a special device that controls the timing and amount of formula given. Formula flows from a feeding bag or pre‑filled container through tubing that runs into the pump and then into your feeding tube.
Used for: Continuous feedings and some intermittent feedings